Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy: What Each Phase Means for Your Vision
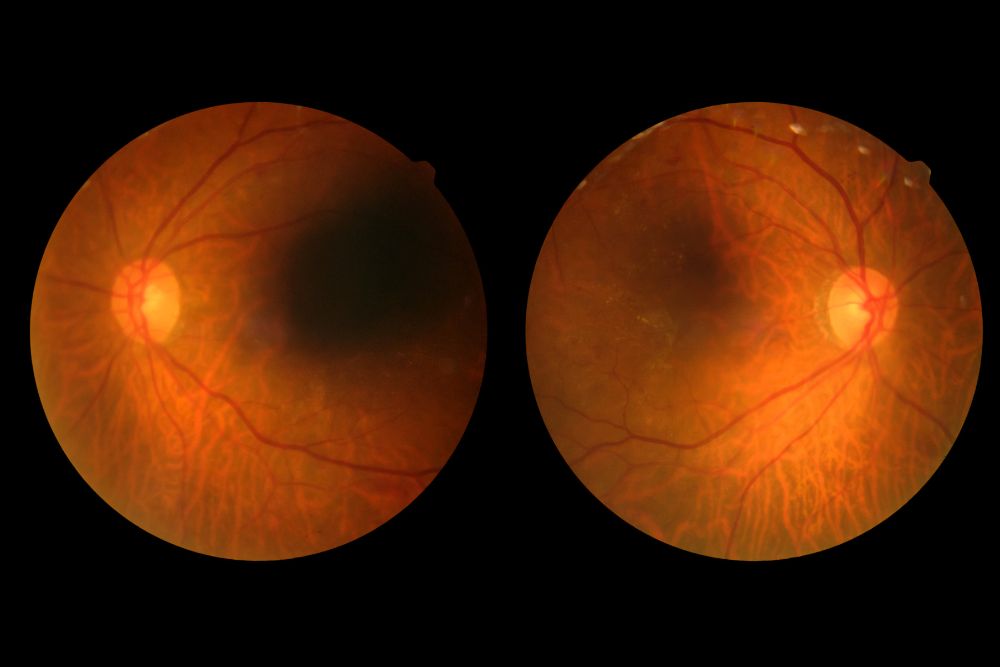
Diabetes affects more than just your blood sugar—it can also damage your eyes. The retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, plays a crucial role in how we see the world. Consistently high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can cause permanent vision loss if left untreated.
Diabetic Retinopathy Progression
Diabetic retinopathy is typically divided into four stages, grouped into two main types: nonproliferative (early) and proliferative (advanced). Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) refers to the early stages of the disease, while proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) describes its advanced form.
Mild NPDR
NPDR is the earliest stage of diabetic eye disease. It's characterized by small areas of swelling in the blood vessels of the retina, known as microaneurysms. Although these microaneurysms may cause small amounts of fluid to leak into the retina, symptoms are usually not noticeable at this stage.
Moderate NPDR
During this stage, the small blood vessels continue to swell, obstructing blood flow to the retina. Symptoms aren’t always noticeable but may include blurry vision.
Severe NPDR
At this stage, larger sections of blood vessels in the retina become blocked, leading to a decrease in blood flow to this area. In response, the body begins to produce new, thin, and fragile blood vessels. Noticeable symptoms include blurry vision, dark spots, and even patches of vision loss. If these new vessels leak into the macula, it can result in sudden and permanent vision loss.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
During this stage, new blood vessels continue to grow within the retina, which can lead to bleeding and the formation of scar tissue in the eye. This scar tissue has the potential to pull the retina away from the back of the eye, causing retinal detachment. Retinal detachment is considered a medical emergency and, if left untreated, can lead to permanent blindness.
Advanced diabetic retinopathy symptoms include:
- Blurry vision
- Colors appearing less vibrant
- Blank or dark areas in the field of vision
- Increase in eye floaters
- Poor night vision
Schedule an Appointment with a Retina Specialist
Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive eye disease that can lead to irreversible vision loss. In the early stages, this condition often doesn't show noticeable symptoms, making it essential for individuals with diabetes or those at risk to schedule regular eye exams. The earlier diabetic retinopathy is caught and treated, the better your chances of protecting your sight.

